3.4 3.4 MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS development
3.4 3.4 MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS development. By: SHOBHA RANI 10-Ph-CA-01. UNIT 1: Introduction to Multimedia Systems Concept of Multimedia:
Share Presentation
Embed Code
Link
Download Presentation
- media
- real time
- web pages
- cd rom
- multimedia chapter 1
- multimedia capable file system

dhubbs + Follow
Download Presentation
3.4 3.4 MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS development
An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.
Presentation Transcript
- 3.4 3.4 MULTIMEDIA APPLICATIONS development By: SHOBHA RANI 10-Ph-CA-01
- UNIT 1:Introduction to Multimedia Systems Concept of Multimedia: Multimedia means that computer information can be represented through audio, video, and animation in addition to traditional media (i.e., text, graphics drawings, images).
- Multimedia is a combination of text, graphic, sound, animation, and video that is delivered interactively to the user by electronic or digitally manipulated means.
- 3.Desirable Features for a Multimedia System • High Processing Power • needed to deal with large data processing and real time delivery of media. Special hardware commonplace. • Multimedia Capable File System • -- needed to deliver real-time media -- e.g. Video/Audio Streaming. Special Hardware/Software needed e.g RAID technology. • Data Representations/File Formats that support multimedia • -- Data representations/file formats should be easy to handle yet allow for compression/decompression in real-time. • Efficient and High I/O • -- input and output to the file subsystem needs to be efficient and fast. Needs to allow for real-time recording as well as playback of data. e.g. Direct to Disk recording systems. • Special Operating System • -- to allow access to file system and process data efficiently and quickly. Needs to support direct transfers to disk, real-time scheduling, fast interrupt processing, I/O streaming etc. • Storage and Memory • -- large storage units (of the order of 50 -100 Gb or more) and large memory (50 -100 Mb or more). Large Caches also required and frequently of Level 2 and 3 hierarchy for efficient management. • Network Support • -- Client-server systems common as distributed systems common. • Software Tools • -- user friendly tools needed to handle media, design and develop applications, deliver media.
- MULTIMEDIA HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS CPU Central Processing Unit (CPU) is an essential part in any computer. It is considered as the brain of computer, where processing and synchronization of all activities takes place. The efficiency of a computer is judged by the speed of the CPU in processing of data. For a multimedia computer a Pentium processor is preferred because of higher efficiency. Monitor The monitor is used to see the computer output. Generally, it displays 25 rows and 80 columns of text. The text or graphics in a monitor is created as a result of an arrangement of tiny dots, called pixels. Resolution is the amount of details the monitor can render. Resolution is defined in terms of horizontal and vertical pixel (picture elements) displayed on the screen. Video Grabbing Card We need to convert the analog video signal to digital signal for processing in a computer. Normal computer will not be able to do it alone. It requires special equipment called video grabbing card and software to this conversion process. This card translates the analog signal it receives from conventional sources such as a VCR or a video camera, and converts them into digital format. Sound Card Today’s computers are capable of creatingthe professional multimedia needs. Not only you can use computer to compose your own music, but it can also be used for recognition of speech and synthesis. It can even read back the entire document for you. But before all this happens, we need to convert the conventional sound signal to computer understandable digital signals. This is done using a special component added to the system called sound card. CD-Rom CD-ROM is a magnetic disk of 4.7 inches diameter and it can contain data up to 680 Megabytes. It has become a standard by itself basically for its massive storage capacity, faster data transfer rate. To access CD-ROM a very special d1rive is required and it is known as CD-ROM drive.
- Adobe CS4 Adobe CS4 is a collection of graphic design, video editing, and web development applications made by Adobe Systems many of which are the industry standard that includes Adobe Dreamweaver Although a hybrid WYSIWYG and code-based web design and development application, Dreamweaver’s WYSIWYG mode can hide the HTML code details of pages from the user, making it possible for non-coders to create web pages and sites.WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) web development software that allows users to create websites with out using Html, everything can be done visually. Adobe Fireworks A graphics package that allows users to create bitmap and vector graphics editor with features such as: slices, the ability to add hotspots etc.) for rapidly creating website prototypes and application interfaces. Gimp Is an alternative to Photoshop and cheaper but not quite as good.
- Google Sketchup SketchUp is a 3D modelingprogram designed for architects, civil engineers, filmmakers, game developers, and related professions. Microsoft Frontpage As a WYSIWYG editor, FrontPage is designed to hide the details of pages’ HTML code from the user, making it possible for novices to easily create web pages and sites. Apple Quicktime QuickTime is an extensible proprietarymultimedia frameworkdeveloped by Apple, capable of handling various formats of digital video, 3D models, sound, text, animation, music, panoramic images, and interactivity. Photoshop Pro Adobe Photoshop, or simply Photoshop, is a graphics editing program developed and published by Adobe Systems. It is the current market leader for commercial bitmap and image manipulation software, and is the flagship product of Adobe Systems. It has been described as “an industry standard for graphics professionals” Microsoft Powerpoint Powerpoint Presentations are generally made up of slides may contain text, graphics, movies, and other objects, which may be arranged freely on the slide. Adobe Flash Player Adobe Flash (formerly Macromedia Flash) is a multimediaplatformthat is popular for adding animation and interactivity to web pages. Originally acquired by Macromedia, Flash was introduced in 1996, and is currently developed and distributed by Adobe Systems. Flash is commonly used to create animation, advertisements, and various web page Flash components, to integrate video into web pages, and more recently, to develop rich Internet applications. Adobe Shockwave Adobe Shockwave (formerly Macromedia Shockwave) is amultimedia player program, first developed by Macromedia, acquired by Adobe Systems in 2005. It allows Adobe Director applications to be published on the Internet and viewed in a web browser on any computer which has the installed.
- 5.Elements of Multimedia • Text • Graphics • Animation • Audio • Video • Menus • Hyperlinks • Virtual Reality
- Chapter 1 : INTRODUCTION TO MULTIMEDIA 1. INTRODUCTION TO MULTIMEDIA CHAPTER 1 2. What is Multimedia? • Derived from the word “Multi” and “Media” – Multi • Many, Multiple, – Media • Distribution tool & information presentation – text, graphic, voice, images, music and etc. 3. Definition of Multimedia • Multimedia is a combination of text, graphic, sound, animation, and video that is delivered interactively to the user by electronic or digitally manipulated means. TEXT AUDIO GRAPHIC VIDEO ANIMATION 4. 5 Elements of Multimedia TEXTTEXT TEXT AUDIO GRAPHIC VIDEO ANIMATION A broad term for something that contains words to express something. Text is the most basic element of multimedia. A good choice of words could help convey the intended message to the users (keywords). Used in contents, menus, navigational buttons 5. TEXTTEXT Example 5 Elements of Multimedia TEXT AUDIO GRAPHIC VIDEO ANIMATION 6. GRAPHICGRAPHIC TEXT AUDIO GRAPHIC
- Multimedia Formats. Multimedia elements (like audio or video) are stored in media files. The most common way to discover the type of a file, is to look at the file extension.Multimedia files have formats and different extensionslike: .swf, .wav, .mp3, .mp4, .mpg, .wmv, and .avi.
- Applications of multimedia CD-Interactive Multimedia Kiosks World Wide Web MMS ENTERTAINMENT EDUTAINMENT COMMUNICATIONS BUSINESS KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER PUBLIC ACCESS
- Applications World Wide Web Hypermedia courseware Video conferencing Video-on-demand Interactive TV Groupware Home shopping Games Virtual reality Digital video editing and pro
- Benefits Is easy to use. 2. Enhancement of Text Only Messages 3. Improves over Traditional Audio-Video Presentations 4. Gains and Holds Attention Entertaining as Well as Educational Cost-effective 8. Trendy Entertaining as Well as Educational
- Expensive 2. Not always easy to configureRequires special hardware 4. Not always compaTIABLE
- Thank You

3.4
518 views • 40 slides

3.4 Applications of Linear Systems
3.4 Applications of Linear Systems. Steps. 1) Read and underline important terms 2) Assign 2 variables x and y (use diagram or table as needed) 3) Write a system of equations 4) Solve for x and y 5) Check answer 6) State answer. Problem with quantities and costs.
243 views • 14 slides

3.4
3.4. The Race for Empires. The Race for Empires. Early French Settlements Jacques Cartier (1534) North coast of N. America Established French settlement @ Florida French Huguenots (driven out by Spanish) French Colonies Religious wars delay colonization of America
325 views • 10 slides

3.4
3.4. Measures of Position and Outliers. The Z-Score. EXAMPLE Using Z-Scores.
448 views • 22 slides

3.4
3.4. Is It A Right Triangle ? Pg. 13 Pythagorean Theorem Converse and Distance . 3.4 – Is It A Right Triangle ?_______________ Pythagorean Theorem Converse and Distance .
371 views • 24 slides

3.4
Measures of Position. 3.4. The standard deviation is a measure of dispersion that uses the same dimensions as the data (remember the empirical rule) The distance of a data value from the mean, calculated as the number of standard deviations, would be a useful measurement
294 views • 16 slides

3.4
Velocity and Acceleration. 3.4. Given that f(t) is a position function relating distance in terms of time. Speed is the absolute value of velocity. Acceleration is the derivative of velocity. Velocity is the first derivative of position. If distance is in:. Velocity would be in:.
287 views • 8 slides

Section 3.4
Section 3.4. Applications. Example 1. A coin bank holds nickels, dimes, and quarters. There are 45 coins in the bank and the value of the coins is $4.75. If there are five more nickels than quarters, find the number of each type of coin in the bank . N = # of nickels D = # of dimes
262 views • 16 slides

3.4
3.4. Properties of Logarithmic Functions. Quick Review. Quick Review Solutions. What you’ll learn about. Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data … and why The applications of logarithms are based on their many
360 views • 20 slides

3.4
3.4. Multiplying Polynomials. Multiplying Monomials. To multiply exponential forms that have the same base, we can add the exponents and keep the same base. In other words…. To Multiply Monomials:. Multiply the Coefficients Add the Exponents of the like variables. Try a few. 4y 5 × 6y 3
389 views • 22 slides
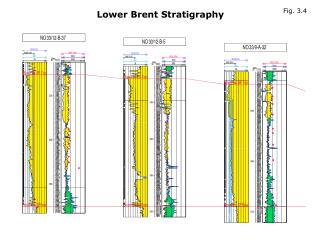
Fig. 3.4
Fig. 3.4. Lower Brent Stratigraphy. Fig. 3.5. Lower Brent Stratigraphy. Fig. 3.6. Lower Brent Stratigraphy. SOUTH. 7. 6. 5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Lithostratigraphic boundary. Sequence stratigraphic boundary (time line). Sequence #. 1. NORTH. 7. 6. 5. 4. 3. Lithostratigraphic boundary.
284 views • 12 slides

3.4 Notes
3.4 Notes. Graphing Rational Functions. 3.4 Notes. Unlike polynomial functions which are continuous, rational functions have discontinuities. Remember the types of discontinuities? jump – assoc. with piece-wise fxns point infinite. 3.4 Notes. Graphing rational functions:
209 views • 7 slides

C.3.4 - Applications of DE
C.3.4 - Applications of DE. Calculus - Santowski. Lesson Objectives. 1. Apply differential equations to applications involving exponential growth & decay, Newton’s Law of Cooling, and introduce the Logistic Equation for population modeling. Fast Five. Solve the following DE:.
362 views • 26 slides

Section 3.4
Chapter 3. Section 3.4. Exercise #5. +. =. =. 1. =. 3. Add. +. =. Chapter 3. Section 3.4. Exercise #11. +. +. =. =. =. Add. +. +. +. +. Chapter 3. Section 3.4. Exercise #17. –. =. =. Subtract. –. =. –. =. Chapter 3. Section 3.4. Exercise #19. –. =. =.
326 views • 27 slides

§ 3.4
Counting Principles. § 3.4. Fundamental Counting Principle. If one event can occur in m ways and a second event can occur in n ways, the number of ways the two events can occur in sequence is m· n . This rule can be extended for any number of events occurring in a sequence.
254 views • 13 slides

3.4
Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers. 3.4. Adding Mixed Numbers. Recall that a mixed number has a whole number part and a fraction part. Adding or Subtracting Mixed Numbers To add or subtract mixed numbers, add or subtract the fraction parts and then add or subtract the whole number parts.
303 views • 17 slides

3.4 Prenatal Development
Prenatal development after the eighth week is the fetal period. This is the time when structures grow and specialize. From the start of the ninth week until birth, the prenatal human organism is a fetus. 3.4 Prenatal Development.
463 views • 43 slides

3.4
3.4. Properties of Logarithmic Functions. Properties of Logarithms. Example Proving the Product Rule for Logarithms. Example Expanding the Logarithm of a Product. Example Expanding the Logarithm of a Product. Example Condensing a Logarithmic Expression.
134 views • 10 slides

3.4
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials. 3.4. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials. To Add Polynomials Combine all the like terms. To Subtract Polynomials Change the signs of the terms of the polynomial being subtracted, and then combine all the like terms. Adding and Subtracting Polynomials.

3.4
3.4. Demana, Waits, Foley, Kennedy. Properties of Logarithmic Functions. What you’ll learn about. Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data … and why The applications of logarithms are based on their many
207 views • 19 slides






















